

Synchronization replicates application files and configuration information between servers. If you are using clusters, synchronization ensures that logical servers in a cluster share the same application files and configuration. Synchronization is also a useful alternative to importing and exporting packages.
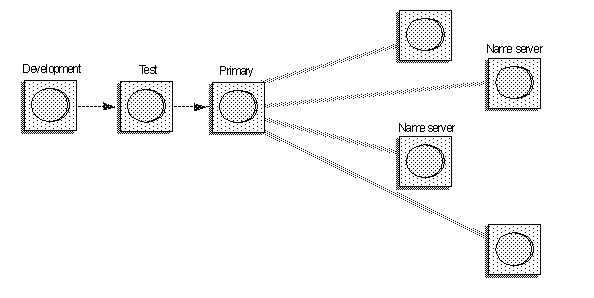
For example, as Figure 6-2 illustrates, you can replicate new components from a testing or development server to one or more production servers. As long as you can connect to both servers, synchronization is quicker and easier than exporting and importing package files.
Figure 6-2: Synchronization example
If you are using clusters and make configuration changes to the primary server, the jagadmin user (or any user with the Admin role) can synchronize those changes to participating nonprimary servers.
To synchronize a cluster, you must be connected to the primary server for the cluster unless the primary server is down and cannot be restarted. In this case, you can connect to another server within the cluster and designate it as the new primary server.
You can use the synchronization option to move repository information between servers that are not part of a cluster. For example, you may want to move a development server’s repository to a test server. In this case, the synchronization command is similar to EAServer’s export/import options without the JAR file; instead of moving packages from one server to another, you are moving repository information.
Synchronization does not propagate deletions. If you delete an entity such as a component or Web application in the source installation, and you have previously replicated the entity by synchronization, you must connect to the target server with EAServer Manager or jagtool and delete the entity manually.
You can synchronize at the cluster, server, servlet, package, or component level. The level you choose determines the available synchronization options. Options that are not available are dimmed, and cannot be selected.
![]() Before you synchronize a cluster, shut down any services
that are running. If you do not, some files required for synchronization
may be locked.
Before you synchronize a cluster, shut down any services
that are running. If you do not, some files required for synchronization
may be locked.
The items that are synchronized for a component are the same in a Java archive (JAR) file, as for a package when using EAServer’s Export feature, and include:
Component definition (component properties)
Interface definition(s)
For C/C++ components, the DLL (or shared library) indicated by the com.sybase.jaguar.component.cpp.library property
For Java and EJB components, the implementation class (property com.sybase.jaguar.component.java.class), any classes referred to by the com.sybase.jaguar.component.java.classes property, plus stub classes listed in the com.sybase.jaguar.component.files.corbastubs, and com.sybase.jaguar.component.files.ejbstubs properties
For PowerBuilder components, the libraries starting with a “$” that are referenced by the com.sybase.jaguar.component.pb.librarylist property
![]() If you are synchronizing PowerBuilder components, the
servers must all use the same PBVM version.
If you are synchronizing PowerBuilder components, the
servers must all use the same PBVM version.
Other files indicated by the com.sybase.jaguar.component.files property.
![]() Synchronizing after deleting or moving
components
Synchronization does not remove components that you have deleted.
You must connect to the target server and delete the component with
EAServer Manager or jagtool. If you move a component
from one package to another, you must delete it from the original
package on the target server.
Synchronizing after deleting or moving
components
Synchronization does not remove components that you have deleted.
You must connect to the target server and delete the component with
EAServer Manager or jagtool. If you move a component
from one package to another, you must delete it from the original
package on the target server.
When you synchronize an EAServer package, these items are distributed to the remote servers:
The same items as for component synchronization for each component in the package.
Java stub classes indicated by com.sybase.jaguar.package.files.corbastubs and com.sybase.jaguar.package.files.ejbstubs properties.
Other files indicated by property com.sybase.jaguar.package.files.
When you synchronize an EAServer servlet, the following items are distributed to the remote servers:
The servlet definition (servlet properties).
The servlet class (property com.sybase.jaguar.servlet.java.class), and any classes referred to by property com.sybase.jaguar.servlet.java.classes.
Other files indicated by property com.sybase.jaguar.servlet.files.
When you synchronize an EAServer application, the following items are distributed to the remote servers:
The application definition (application properties)
The packages, Web applications, and the other resources contained in the application
When you synchronize an EAServer Web application, the following items are distributed to the remote servers:
The Web application definition (Web application properties).
The servlets, JSPs, and filters installed in the Web application, including implementation classes and properties.
By default, the Java classes listed in the Web application’s custom class list specified on the Java Classes tab in the EAServer Manager Web Application Properties dialog box. You can disable synchronization of these files in the synchronization options described in Table 6-1.
The Web application’s context root directory and its contents.
Files specified on the Additional Files tab in the Web Application Properties dialog box in EAServer Manager (or by the com.sybase.jaguar.webapplication.files property if using jagtool).
You can synchronize servers and application components from EAServer Manager or by using the jagtool sync command.
![]() Synchronizing a cluster
from EAServer Manager
Synchronizing a cluster
from EAServer Manager
Use EAServer Manager to connect to the source (primary) server.
Depending on the level of the sync operation, highlight a cluster, server, package, servlet, or component.
![]() Synchronization is enabled for servers, packages, and
components for any EAServer edition. Cluster synchronization is
enabled only for the Enterprise Edition. The cluster options display
in the Synchronize dialog for any object, but are disabled if the
Enterprise Edition is not licensed.
Synchronization is enabled for servers, packages, and
components for any EAServer edition. Cluster synchronization is
enabled only for the Enterprise Edition. The cluster options display
in the Synchronize dialog for any object, but are disabled if the
Enterprise Edition is not licensed.
Select File | Synchronize.
Supply the synchronization information in the Synchronization dialog and click Start Sync. Table 6-1 describes the synchronization properties.
A server is in Admin mode if it is running and accepting connections from EAServer Manager, but not accepting ordinary client connections. A server in Admin mode can be the target of synchronization, since this is often the appropriate way to get it out of Admin mode. EAServer Manager warns you if you connect to a server that is running in Admin mode. You can force a server into Ready mode as described in “Switching to Ready mode”, but you should understand why the server is in Admin mode before you use this option.
Property |
Description |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
Username |
The user name used to log in to the remote servers. |
The user must belong to the Admin Role to use the synchronize option. |
Password |
The password for the user name on the remote servers. |
When synchronizing to multiple remote servers, including cluster members, all remote servers must use the same password to allow connection to those servers. |
Cluster |
Click the Cluster check box and select a cluster from the drop-down list to synchronize the entire cluster. |
If you are synchronizing a server, package, component, or servlets, you can specify that the changes be replicated to all servers in a cluster. Use this option only when connected to the cluster's primary server, or when connected to a nonprimary server that becomes the primary after synchronization. |
Servers |
Click the Servers check box and supply a list of one or more URLs to be targets of synchronization if you want to synchronize a subset of the cluster. |
The URLs must be separated
by a comma, and of the form |
All Web App Files |
When this option is selected, all Web application files are distributed to the remote servers. |
See “Web application synchronization” for more information. |
Synchronize Java Classes |
Applies to Web application synchronization only. Specifies whether to synchronize Java classes listed in the Web application’s custom class list specified on the Java Classes tab in the EAServer Manager Web Application Properties dialog box. |
|
All Package Files |
When this option is selected, all of the package files are distributed to the remote servers. Package files refers to all user-defined IDL files, property files, and implementation files (Java .class, .dll, .so, .pbd) based on component definitions. |
Selecting this option may result in the synchronization taking a long time, depending on the number of files being transferred to the remote server(s). Consider using component-level synchronization if only a few components have been changed. See “Component synchronization” and “Package synchronization” for more information. |
All Servlet Files |
When this option is selected, all servlet files are distributed to the remote servers. |
See “Servlet synchronization” for more information. |
All App Files |
When this option is selected, all application files are distributed to the remote servers. |
See “Application synchronization” for more information. |
All Connector Files |
When this option is selected, all connector files are distributed to the remote servers. |
|
All Files Matching the Wildcard Pattern |
When this option is selected, all files that match the wildcard pattern you enter in the adjacent field are distributed to the remote servers. |
|
Verbose |
Run in verbose mode. |
|
Refresh |
If you select this option, the servers you are synchronizing refresh when synchronization completes. |
|
Restart |
If you select this option, the servers you are synchronizing restart when synchronization completes. |
A timeout is used so that if a remote server does not restart, the synchronization moves to the next server. |
Then Wait |
This is the amount of time that the primary waits for a server to restart if you have selected the Restart option. |
![]() Overriding synchronization operations
Overriding synchronization operations
You may want to manually configure properties on individual servers in a cluster to override properties from the logical server definition. For example, you may want to:
Increase the size of a connection cache on a machine that has more memory than other machines.
Establish a process for making manual updates after each EAServer Manager synchronization.
| Copyright © 2005. Sybase Inc. All rights reserved. |

|
|